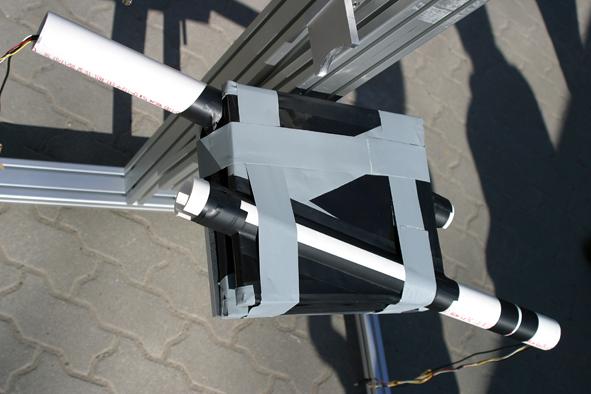
To measure the rate of the muons that come from the atmosphere to the ground, we set up an experiment using scintillators and photomultipliers.
A photomultiplier is a detector, which in our case is connected to a scintillator material.
When a muon enters the scintillator, it excites atoms from the scintillator, that emit a photon. The photons are detected by the attached photomultilplier, which converts them into an electrical signal and transmits it to a DAQ card. There it is digitized, timestamped and afterwards transfered to a computer, and, more precisely, to the program „QuarkNet“, where is recorded.
There is always an amount of „noise“, events detected in the photomultiplier which are not coming from muons but from other energy sources (for example from the thermal noise). To distinguish muons and noise, we set up a „muon telescope“, that is, two (or more) scintillators forming a line. Only if we had nearly simultaneous signals from all the scintillators, that was a muon which went through all the detectors. Otherwise, it was noise.
Another way to eliminate noise is to set „tresholds“. Simply, a „treshold“ tells the program to ignore all the signals below a certain amplitude. Since the scintillators and the photomultiplier have different ages, I had to calibrate tresholds so, that all the scintillators detected a nearly equal event rate (around 40 Hz).
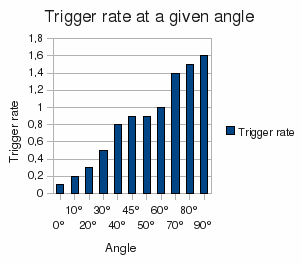
With the use of a rotating structure, I
set up measurements at different zenith angles and the result was
that the upright turning angle received more muons than the
horizontal one. That's because the muon comuing from the side have to
pass trough a lot more of atmosphere. Thus they loose more energy and
have a higher probability to decay before reaching the detector (they
are slower so their time dilation is shorter)