The production of Drell-Yan pairs in polarized nucleon-nucleon
collisions can provide information on a variety of polarized structure
functions in dependence on the relative orientation of the beam and
target polarization directions.
The longitudinal double spin asymmetry
turns out to be well suited to extract the
polarized light sea-quark distribution
![]()
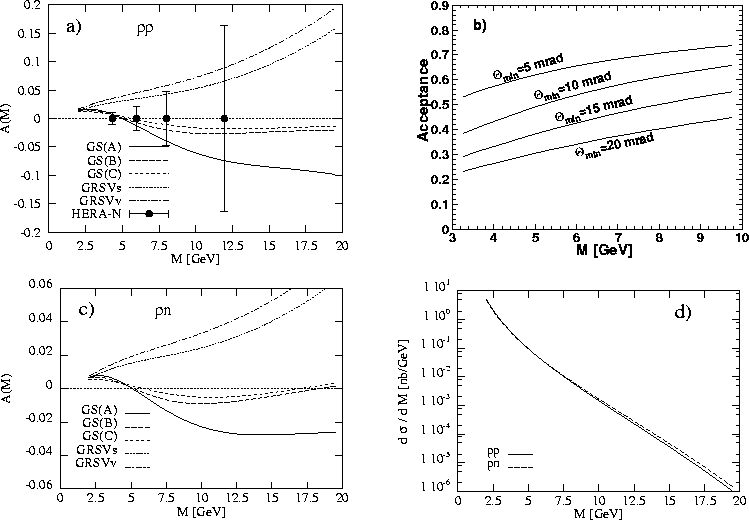
Figure 3: Expected longitudinal double spin asymmetries in the polarized
Drell-Yan process for a) pp and c) pn collisions (![]() GeV)
from Ref. [28] confronted
to the projected statistical errors expected for HERA-
GeV)
from Ref. [28] confronted
to the projected statistical errors expected for HERA-![]() .
b) the acceptance for lepton pair registration in a particular detector
with minimal registration angle
.
b) the acceptance for lepton pair registration in a particular detector
with minimal registration angle ![]() .
d) the unpolarized cross-section of the Drell-Yan process for pp and
pn collisions [28].
.
d) the unpolarized cross-section of the Drell-Yan process for pp and
pn collisions [28].
The prospects for such a measurement at HERA-![]() were calculated in ref. [28] at next-to-leading order QCD.
The spread of the predictions (see fig. 3a,c) reflects
the insufficient present knowledge on the polarized sea quark
distributions in the region x > 0.1; not even the sign of the
asymmetry at large M is predicted. Since the asymmetry is the weighted
sum of
were calculated in ref. [28] at next-to-leading order QCD.
The spread of the predictions (see fig. 3a,c) reflects
the insufficient present knowledge on the polarized sea quark
distributions in the region x > 0.1; not even the sign of the
asymmetry at large M is predicted. Since the asymmetry is the weighted
sum of ![]() and
and ![]() quarks with the strange
quark contribution assumed to be small and the weight of
quarks with the strange
quark contribution assumed to be small and the weight of ![]() is higher than that of
is higher than that of ![]() due to its abundance in the
proton and the electric charge, the asymmetry measured in pp collisions
provides mainly
information on
due to its abundance in the
proton and the electric charge, the asymmetry measured in pp collisions
provides mainly
information on ![]() , i.e. on the u sea quark polarization.
The flavour contributions are slightly different for pn collisions;
this results in an asymmetry being much smaller (fig. 3c) than in the pp
case. Since the total unpolarized cross-sections for the Drell-Yan process
in pp and pn
collisons are practically the same (see fig. 3d)
much larger luminosity is required in pn collisons to obtain a reasonable statistical
sensitivity. Nevertheless,
it is very important as it could be used to decompose the flavour
structure of the polarized sea which is practically unknown at present.
, i.e. on the u sea quark polarization.
The flavour contributions are slightly different for pn collisions;
this results in an asymmetry being much smaller (fig. 3c) than in the pp
case. Since the total unpolarized cross-sections for the Drell-Yan process
in pp and pn
collisons are practically the same (see fig. 3d)
much larger luminosity is required in pn collisons to obtain a reasonable statistical
sensitivity. Nevertheless,
it is very important as it could be used to decompose the flavour
structure of the polarized sea which is practically unknown at present.
Also, with a larger luminosity more information could be obtained from measuring
the differential lepton pair distributions in dependence on ![]() or
or
![]() [28, 29], the predictions for the
[28, 29], the predictions for the ![]() dependence are
shown in fig. 4.
dependence are
shown in fig. 4.
We note that the acceptance for lepton pair detection
was not taken into account in the calculations [28] as it depends
on the particular detector. The acceptance (integrated over kinematical
parameters of produced pairs) depends mainly on the minimal
accepted lepton angle in the detector (see fig. 3b);
a value of about 50% may be realistic. In this case the projected
statistical sensitivity values, shown in fig. 3a, would be larger
by a factor of ![]() .
.
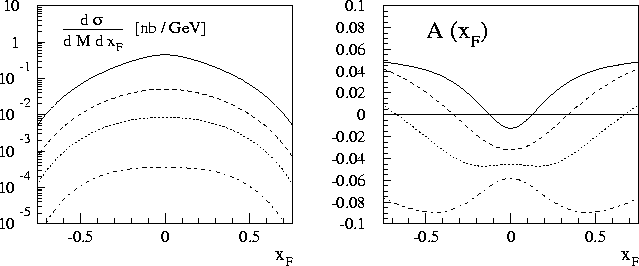
Figure 4: The unpolarized Drell-Yan cross-section and the asymmetry in pp collisions
for the polarized GS(A) parton distributions. Curves are for different
invariant masses M: solid - 4 GeV; dashed - 6 GeV; dotted - 8 GeV;
dot-dashed - 12 GeV. The figures are from Ref. [29]).
Drell-Yan pair production with transverse polarization of
both beam and target can provide a measurement of the transversity
distribution, ![]() .
The transverse double spin asymmetry in nucleon-nucleon
Drell-Yan production
can be schematically written in the form [30]
.
The transverse double spin asymmetry in nucleon-nucleon
Drell-Yan production
can be schematically written in the form [30]
![]()
where ![]() is the polar angle of one lepton in the virtual photon
rest frame and
is the polar angle of one lepton in the virtual photon
rest frame and ![]() is the angle between the direction of
polarization and the normal to the dilepton decay plane.
An estimate of the asymmetry for HERA-
is the angle between the direction of
polarization and the normal to the dilepton decay plane.
An estimate of the asymmetry for HERA-![]() energy was given recently
[31] from both LO and NLO calculations.
One should stress, however, that the anticipated asymmetry level strongly
depends on the actual size of the transversity distributions, which
are totally unknown at present. Although in the non-relativistic quark model
the relation
energy was given recently
[31] from both LO and NLO calculations.
One should stress, however, that the anticipated asymmetry level strongly
depends on the actual size of the transversity distributions, which
are totally unknown at present. Although in the non-relativistic quark model
the relation ![]() holds, in reality differences
between both distributions are expected to be caused by dynamical effects.
Due to the lack of any information on the transversity distribution, the
maximally possible value of the asymmetry was estimated [31];
the corresponding results on LO and NLO polarized Drell-Yan cross-section and asymmetry
are presented at fig. 5. The projected statistical errors for
a measurement of
holds, in reality differences
between both distributions are expected to be caused by dynamical effects.
Due to the lack of any information on the transversity distribution, the
maximally possible value of the asymmetry was estimated [31];
the corresponding results on LO and NLO polarized Drell-Yan cross-section and asymmetry
are presented at fig. 5. The projected statistical errors for
a measurement of ![]() at HERA-
at HERA-![]() are also shown. The maximal value
of
are also shown. The maximal value
of ![]() at an invariant mass of M=4 GeV was found to be approximately
at an invariant mass of M=4 GeV was found to be approximately ![]() with an expected statistical error
of about
with an expected statistical error
of about ![]() . The expected value of the asymmetry
at RHIC energies is smaller but the statistical errors become relatively
smaller at
. The expected value of the asymmetry
at RHIC energies is smaller but the statistical errors become relatively
smaller at ![]() GeV due to the higher luminosity of
GeV due to the higher luminosity of ![]() pb
pb![]() [31].
[31].
The calculations [31] do not account for the acceptance of the lepton pair
in the detector. The same discussion as above for the LL case applies here.
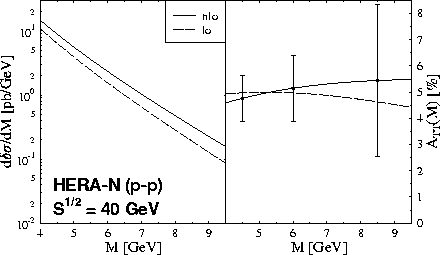
Figure 5: Maximal polarized Drell-Yan cross-section (left figure)
and the asymmetry (right figure) in double transverse polarized collisions
as a function of the invariant mass. The results are shown
for both LO and NLO calculations [31].
The projected statistical errors for HERA-![]() are shown, as well.
are shown, as well.
We note that there exist another potentially interesting
possibility, the study of the longitudinal-transverse
double spin asymmetry, ![]() .
This asymmetry was calculated in
ref. [30] and depends in a rather complicated fashion
on both twist-2 (
.
This asymmetry was calculated in
ref. [30] and depends in a rather complicated fashion
on both twist-2 (![]() and
and ![]() ) and twist-3 (
) and twist-3 (![]() and
and ![]() ) polarized
structure functions. In contrast to
) polarized
structure functions. In contrast to ![]() and
and ![]() the asymmetry
the asymmetry ![]() decreases as
decreases as ![]() .
The expected level of the asymmetry
.
The expected level of the asymmetry ![]() at HERA-
at HERA-![]() energy
has not been calculated yet, the expected level of sensitivity
as a function of the lepton pair mass can be taken from fig. 3.
energy
has not been calculated yet, the expected level of sensitivity
as a function of the lepton pair mass can be taken from fig. 3.